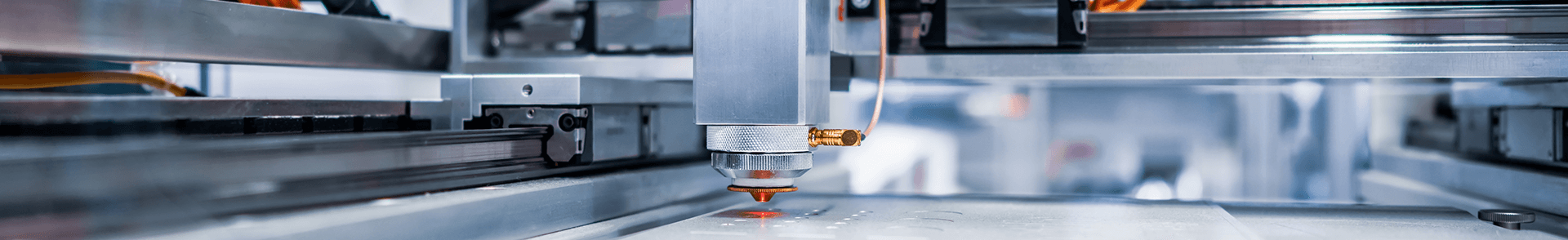
Laser cutting and engraving are two closely related processes that utilize high-powered lasers to precisely cut or engrave materials. Here's a closer look at each process:
Laser cutting: Laser cutting involves using a laser beam to cut through a material along a pre-determined path. The laser beam melts, burns, or vaporizes the material, resulting in a clean and precise cut. Laser cutting is commonly used in various industries, including manufacturing, fabrication, and crafts. It can cut a wide range of materials such as metal, wood, acrylic, paper, fabric, and more. The process is controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) systems, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
Laser engraving: Laser engraving, on the other hand, is the process of using a laser beam to remove material from the surface of an object in order to create a permanent mark, design, or inscription. The laser beam interacts with the material, causing it to vaporize or change its physical properties, resulting in a visible engraving. Laser engraving is commonly used for personalizing items, creating signage, branding products, and adding intricate details to various materials such as wood, glass, metal, plastic, leather, and more
Laser Cutting Methods

Much like specific laser types are employed for different purposes, manufacturers can use several unique laser cutting methods to achieve desirable effects. Here are some of them:
Melt and blow — Also known as fusion cutting, this method uses high-pressure gas to produce the results. First, the machine heats the material to a melting point and then blows the molten material out of the kerf.
Stealth dicing of silicon wafers — This method separates a small block of semiconducting material (called a die) from a wafer of a semiconductor. In this particular case, a pulsed Nd: YAG laser with the wavelength adapted to the electronic bandgap of silicon performs the procedure.
Reactive cutting — Often called "flame cutting," this method uses a laser beam as the ignition source to cut very thick steel plates. It is similar to oxygen torch cutting.
Thermal stress cracking — This method takes advantage of thermal fracture, using a beam to create cracks in brittle materials, like glass.
Vaporization cutting — In this method, the focused beam heats the material to a flashpoint. It creates a keyhole that is further enlarged by vapor generated by the beam. This vapor also blows eject out, allowing the hole to increase in size even more.
What Is Laser Engraving?

Laser engraving, although to some extent similar to laser cutting, is a process intended to achieve entirely different goals. Instead of cutting the material into a specific shape, it is about engraving a shape, graphic, or picture on a particular surface.
Laser engravers usually generate a beam with decreased intensity than laser cutters. It makes it easier to avoid cutting too much of the material. The power produced by the laser should be just enough to leave a mark without cutting the object all the way through.
A laser engraving machine, much like a laser cutter, consists of three main parts:
a laser
a controller
a surface
The primary difference between an engraver and a cutter is that the former features a lens with a shorter focal length. It provides a finer spot size for working with materials like plastic and wood.
We can distinguish two subgroups of laser engravers: stationary and non-stationary. Non-stationary laser engravers move over the desired engraving area, much like an ink printer over a piece of paper. This way, the laser can cover a larger surface area. Conversely, stationary laser engravers do not move. The advantage of this method is that the machine works faster and at higher power.
What Kinds of Materials Can Be Engraved?
The most frequently used materials in the engraving are metal and wood. Still, pretty much everything can be engraved — provided it offers a hard enough surface for the machine to work with. As a result, it is not surprising to see engravings on glass, leather, plastic, and fiber.
Softer materials (e.g., wood, plastic) require less power, while more rigid materials (e.g., steel) need to be treated with a higher-power beam to leave a long-lasting mark.
If you are interested in entering the world of laser machines, an excellent way to start is to determine what you actually want to do. Do you want to cut some objects out of metal, engrave something on them, or both? Moreover, do you want to work with metal, or do you plan to use wood or plastic? Answering these questions will help you pick the best type of laser cutting machine for you.
Another thing worth considering is the machine's average lifespan, power, and the size of its work area. After all, you need different equipment for putting various shapes on wooden plates than if you were to work with plastic cutlery. Considering the average life of a laser tube spanning between 8000 to 10,000 hours, you can expect around three months of continuous operation out of yours. As long as you want to use your machine only for hobby-related purposes, it should be a sufficient amount.