For years, laser cutting has been a game-changer across various industries, thanks to its unmatched precision and flexibility. But have you ever wondered how this incredible technology actually operates? In this blog, we'll take a deep dive into the laser cutting process, exploring everything from the key components of a laser cutter to the software options available and the essential safety measures you need to consider.
By gaining insight into the laser cutting process, you'll discover the immense potential it holds for both industrial applications and creative projects. Keep reading to uncover the fascinating details of how laser cutting works.
The Science Behind Laser Cutting: How Do Lasers Cut Materials?
Laser cutters work by emitting a focused beam of high-energy light onto the surface of a material. This concentrated energy heats up and either vaporizes or melts the material, allowing for precise cuts along a predetermined path. As the cutting process unfolds, control systems guide the movement of the laser beam, while assist gases help to clear away debris and ensure clean, smooth edges.
Key Components of a Laser Cutter
A typical laser cutter consists of several essential components:
Laser Source
The laser source is the heart of a fiber laser cutting machine, acting as the "engine" that powers the cutting operation. It generates the laser beam by using specialized gas, liquid, or solid-state materials. Fiber lasers, in particular, offer superior efficiency, longer lifespan, reduced maintenance, and lower operational costs compared to other types of lasers.
Laser Optics
Laser optics are the optical components within the system that shape, direct, and focus the laser beam onto the material. The quality and precision of these optics play a crucial role in determining the success of the cutting process.
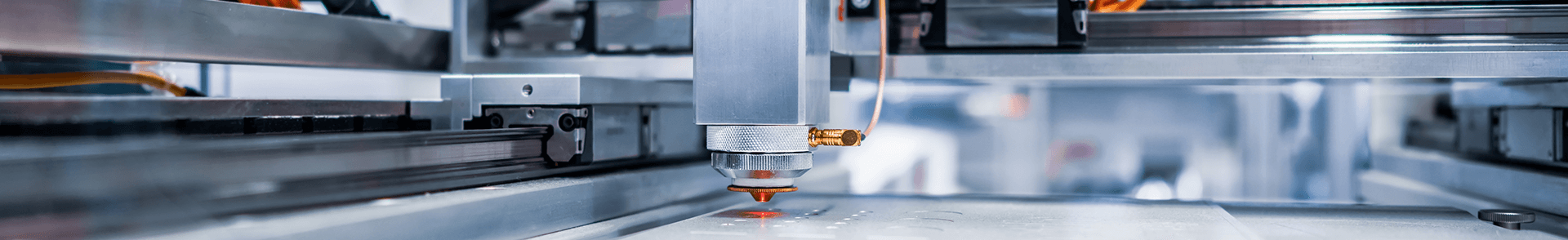
Laser Cutting Head
The laser cutting head is the component responsible for delivering the laser beam to the material. It includes the nozzle, focus lens, and a focus tracking system. The cutting head follows the programmed cutting path, with its height and focus adjusted according to the material’s type and thickness.
Control System
The control system is the brain of the laser cutter, managing and regulating its various functions to ensure precise and efficient cutting. It includes both hardware and software elements that work in tandem to control the laser source, beam delivery, and cutting head movements.
Assist Gas System
Some laser cutters utilize assist gases like oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air to enhance the cutting process. These gases help to blow away molten material and debris, improving cut quality and performance. The assist gas system typically allows for precise control over gas flow and pressure to optimize results for different materials.
The Laser Cutting Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Here’s an overview of how the laser cutting process typically unfolds:
Design Preparation
Start by creating a design using computer-aided design (CAD) software, which defines the shape and dimensions of the cut. The design serves as a blueprint for the laser cutting process, providing exact instructions for the cut’s appearance, size, and other critical details.
Material Setup
Place the material on the laser cutter's bed, securing it with clamps or a vacuum table to ensure stability during cutting. It’s important to clean the material's surface to avoid any interference with the laser.
Laser Beam Emission
Configure the laser cutting machine with the appropriate settings for power, speed, and focus, depending on the material’s type and thickness. The laser beam is then directed onto the material’s surface through mirrors and lenses, initiating the cutting process.
Material Cutting
As the laser beam contacts the material, it heats it to the point of melting, vaporization, or combustion along the defined cutting path. The control system precisely maneuvers the laser beam according to the design file.
Cooling and Finishing
Assist gases may be used to blow away molten material and prevent re-solidification, ensuring a clean cut. Once cutting is complete, the material is removed from the cutting bed, and any necessary finishing or post-processing steps are performed.
Popular Software Options for Laser Cutting
Here are some of the top software choices for designing and preparing files for laser cutting:
CAD Software
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software are widely used to create designs and prepare files for laser cutting. These tools help generate tool paths and optimize cutting settings, making the manufacturing process more efficient.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a leading CAD software that allows users to create detailed 2D and 3D designs. These designs can be easily exported in formats like DXF or DWG, which are compatible with laser cutting machines.
Adobe Illustrator
Adobe Illustrator is a premier vector graphics software favored by professionals for its versatility and powerful features. It supports various file formats, including SVG, PDF, and EPS, making it ideal for creating intricate designs for laser cutting.
Inkscape
Inkscape is a free, open-source vector graphics editor that offers a wide range of tools and features similar to those found in paid software. Its compatibility with SVG files makes it a popular choice for laser cutting workflows.
Safety Considerations in Laser Cutting
Operating laser cutting equipment involves risks, making it vital to follow safety precautions and use the appropriate protective gear:
Safety Glasses
Laser safety glasses are a must to protect your eyes from direct or scattered laser light. They are specifically designed to filter out harmful wavelengths and prevent severe eye injuries.
Protective Clothing
Wearing protective clothing is essential to safeguard your skin from burns. Since you’re working with high-intensity laser beams, make sure all exposed skin is covered with non-flammable materials.
Ventilation System
Laser cutting generates fumes and particles that can be hazardous if inhaled. Proper ventilation and exhaust systems are crucial to remove these contaminants, ensuring a safe work environment.
Fire Safety
Laser cutters can ignite fires if not properly managed. Implementing strict safety protocols and closely monitoring operations is key to preventing fire hazards.
Operator Training
Adequate training is crucial for safely operating laser cutting machines. Operators should undergo comprehensive training programs to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge.
Material Compatibility
Always use materials approved for laser cutting, and avoid those that may produce toxic fumes or harmful reactions when cut with a laser.
Conclusion
Laser cutting is an incredibly precise and versatile process that harnesses the power of focused light to cut various materials with remarkable accuracy. By utilizing advanced software and technology, intricate designs can be executed with ease. However, to fully benefit from its potential, safety must always be a top priority.
At Argus Laser, we adhere to strict safety standards and best practices in all our operations. Our laser cutting specialists use state-of-the-art equipment to ensure the best possible results. Contact us today to learn more about our services!