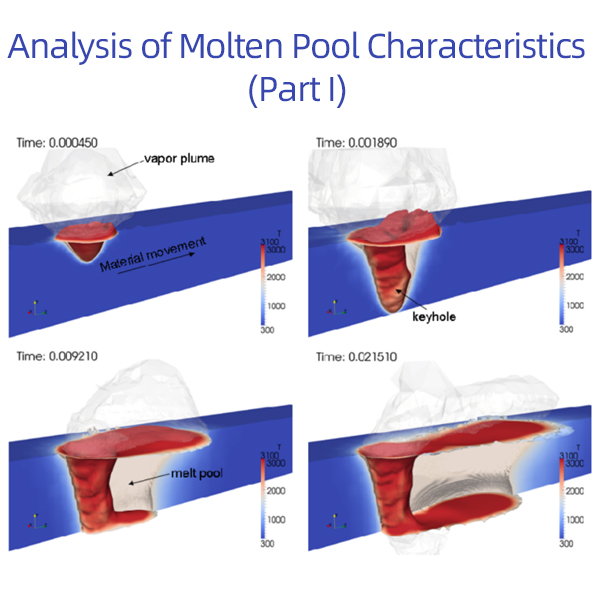
01 Introduction
In modern manufacturing, laser welding technology is widely used in various fields such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, electronic devices, and medical instruments due to its high efficiency, precision, and strong adaptability. The core of this technology lies in the interaction between the laser and the material, forming a molten pool that rapidly solidifies, thereby achieving the connection of metal parts. As a key area in the laser welding process, the characteristics of the molten pool directly determine the welding quality, microstructure, and final performance. Therefore, understanding and accurately controlling the characteristics of the molten pool are crucial for improving laser welding technology and meeting the industry's demand for high-quality welded joints.
02 Molten Pool Geometry
The geometry of the molten pool is an important aspect of laser welding research because it directly affects heat transfer, material flow, and the final welding quality. The geometry of the molten pool is usually described by parameters such as depth, width, aspect ratio, heat-affected zone (HAZ) shape, keyhole shape, and molten metal area (MMA) shape. These parameters not only determine the size and shape of the weld joint but also affect the heat cycle, cooling rate, and microstructure formation during the welding process.
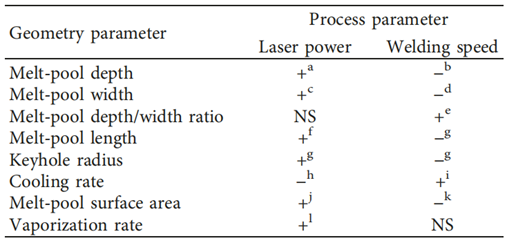
Figure 1. Effect of laser welding parameters on various molten pool geometry parameters.
Research shows that laser power and welding speed are the two main process parameters that affect the geometry of the molten pool, as shown in Figure 1. Generally, as the laser power increases and welding speed decreases, the depth of the molten pool increases, while the width changes relatively little. This is because higher laser power provides more energy, causing the material to melt and vaporize faster, thereby forming a deeper keyhole and molten pool, as shown in Figure 2. However, when the laser power is too high or the welding speed is too low, it may lead to material overheating, excessive vaporization, or even the plasma shielding effect, which can reduce the welding quality. Therefore, in actual welding, laser power and welding speed must be carefully selected based on specific material characteristics and welding requirements to achieve the ideal molten pool geometry.
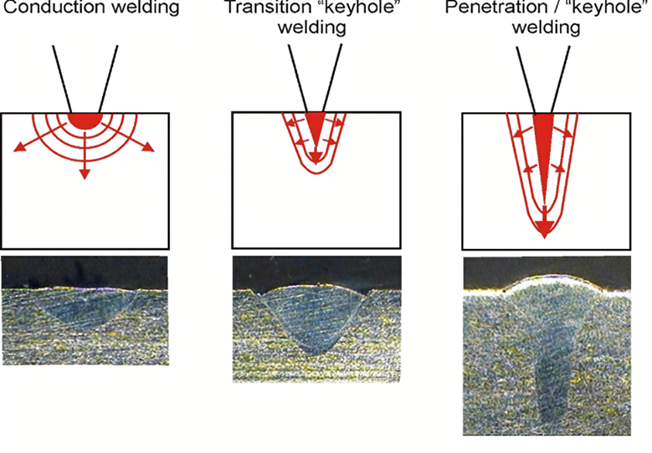
Figure 2. Different weld shapes formed by laser conduction welding and laser deep penetration welding.
In addition to laser power and welding speed, factors such as the material's thermal physical properties, surface conditions, and shielding gas also affect the geometry of the molten pool. For example, the higher the material’s thermal conductivity, the faster heat is transferred within the material, and the faster the cooling rate of the molten pool, which may result in a smaller molten pool size. The surface roughness and cleanliness of the material affect the absorption rate of the laser, thereby influencing the formation and stability of the molten pool. Furthermore, the type and flow rate of the shielding gas also affect the shape and quality of the molten pool. Appropriate shielding gas can effectively prevent oxidation and contamination of the molten pool and adjust the surface tension and flow characteristics, thereby improving welding quality.
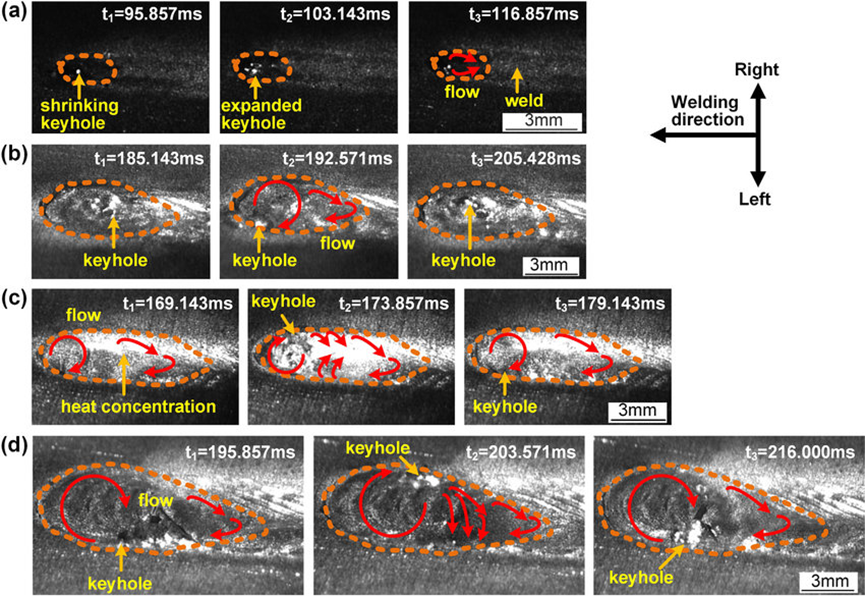
Figure 3. Molten pool shape during laser oscillation.
By changing the movement trajectory of the laser beam, laser oscillation can significantly affect the shape and characteristics of the molten pool, as shown in Figure 3. When the laser beam oscillates, the shape of the molten pool becomes more uniform and stable. The oscillating laser beam forms a wider heating area on the molten pool surface, making the edges of the molten pool smoother and reducing sharp edges and irregular shapes. This uniform heating method helps improve the quality and mechanical properties of the welded joint and reduces welding defects such as cracks and pores. In addition, laser oscillation can also increase the fluidity of the molten pool, promoting the expulsion of gases and impurities from the molten pool, further improving the density and uniformity of the weld.
03 Molten Pool Dynamics
The thermodynamics of the molten pool is another key area of laser welding research. It involves the absorption, transfer, and conversion of laser energy within the molten pool, as well as the resulting temperature field distribution, cooling rates, and phase change behaviors. The thermodynamic properties of the molten pool not only determine its shape and size but also directly affect the microstructure and mechanical properties of the welded joint.
During the laser welding process, once the laser energy is absorbed by the material, a high-temperature region is created in the molten pool, causing the material to melt and vaporize. At the same time, heat is transferred from the high-temperature region to the low-temperature region through conduction, convection, and radiation, increasing the temperature of the surrounding material and affecting the material's microstructure and performance. Due to the small size of the molten pool, the large temperature gradient, and the rapid cooling rate, it is very difficult to directly measure the temperature field and cooling rate inside the molten pool. Therefore, most studies use mathematical models and numerical simulation methods to analyze the thermodynamic properties of the molten pool.
In molten pool thermodynamic models, several key factors need to be considered: first is the laser energy absorption mechanism, including the material surface's reflection, absorption, and transmission characteristics, as well as the scattering and absorption of the laser inside the material. Different materials and laser parameters lead to different absorption rates and energy distributions, which in turn affect the thermodynamic behavior of the molten pool. Next, the material’s thermal physical properties, such as specific heat, thermal conductivity, and density, all change with temperature and have an important influence on heat transfer. In addition, the fluid flow and phase change processes within the molten pool, such as melting, vaporization, and solidification, must also be considered, as these processes alter the shape and temperature field distribution of the molten pool and affect the material's microstructure and mechanical properties.
Through numerical simulation and experimental research, it has been found that the temperature field distribution within the molten pool is usually non-uniform. The high-temperature region is primarily concentrated near the laser interaction zone and keyhole, with the temperature gradually decreasing toward the molten pool edges and heat-affected zone. The cooling rate increases as the molten pool size decreases and as the distance from the laser interaction area increases. Typically, the cooling rate is slower in the molten pool center and keyhole area, while the cooling rate is higher near the molten pool edges and heat-affected zone, as shown in Figure 4. This non-uniform temperature field and cooling rate distribution causes the microstructure of the welded joint to exhibit obvious gradient changes, such as grain size, phase composition, and distribution, which affect the mechanical and corrosion resistance properties of the weld.
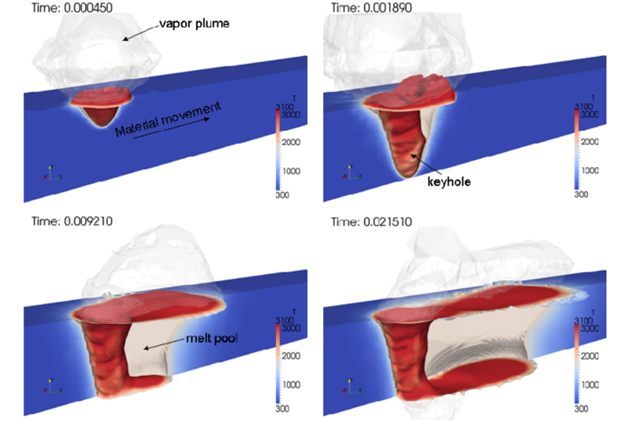
Figure 4. Simulation results of keyhole and molten pool formation in laser deep penetration welding of stainless steel plates.
To improve the thermodynamic properties of the molten pool, enhance welding quality, and reduce welding defects, researchers have proposed various optimization methods. For example, by adjusting laser parameters such as laser power, welding speed, and spot diameter, the energy input and distribution can be modified, optimizing the molten pool's temperature field and cooling rate. Additionally, techniques such as preheating, post-heating, multi-pass welding, and using different shielding gases and welding atmospheres can adjust the thermodynamic behavior and microstructural evolution of the molten pool. Developing new welding materials and alloy systems that improve the material's thermal stability and welding performance is also an important way to enhance the molten pool's thermodynamic properties.
04 Conclusion
The characteristics of the laser welding molten pool are key factors affecting welding quality, microstructure, and mechanical properties. In-depth study of the molten pool's geometry and thermodynamic properties is crucial for optimizing laser welding processes and improving welding efficiency and quality. Through extensive experimental and numerical simulation research, significant achievements have been made, providing strong theoretical support and technical guidance for the development and application of laser welding technology. However, there are still some shortcomings in the current research, such as the simplifications and assumptions in models, and the inability to accurately predict molten pool characteristics under complex conditions. The systematic and comprehensive nature of experimental research still needs improvement, and there is a lack of in-depth studies on more materials and welding parameters.
**--Cite the article published by 高能束加工技术 on January 30, 2025, in the WeChat public account "High-Energy Beam Processing Technology and Applications."