Transportation: all vehicle products have a DataMatrix ID code, usually 2D
Household Appliances: all household appliances (the up-market ones) are laser marked: washing machines, microwave ovens, ovens, stove tops, etcetera
Faucets: the logos on faucets, both writing or designs, are made using a laser marker
Kitchen tools: glasses, forks, knives, pots, and even some types of plates are decorated with the manufacturer’s logo made using a laser marker
Medicine and orthodontics: medical tools - for the patient’s safety - are identified with a code that is usually made using a Picosecond laser
Fashion accessories: belts, buckles, earrings, rings, and more, are all laser marked so that the symbol is indelible and will last forever, like a diamond
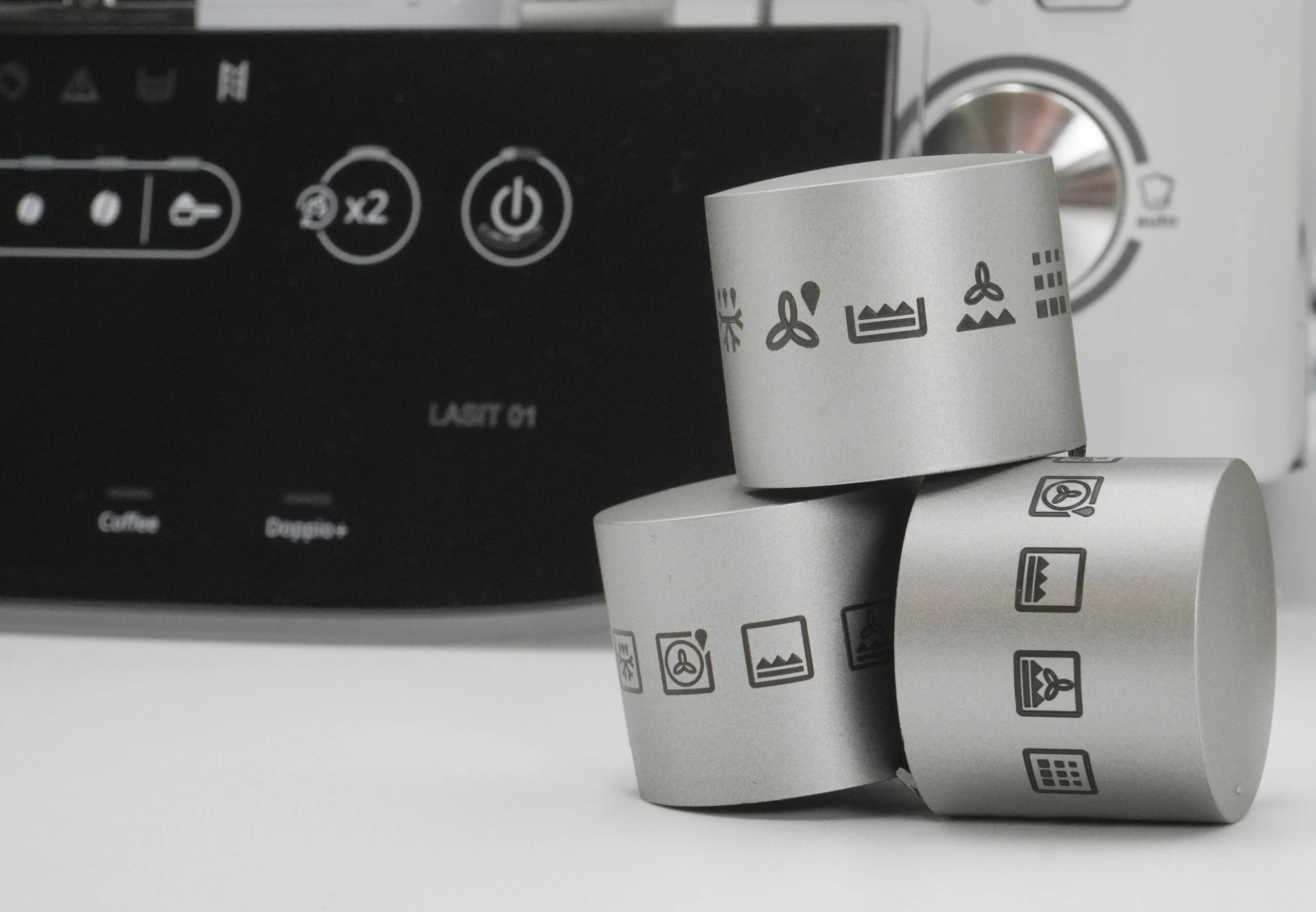


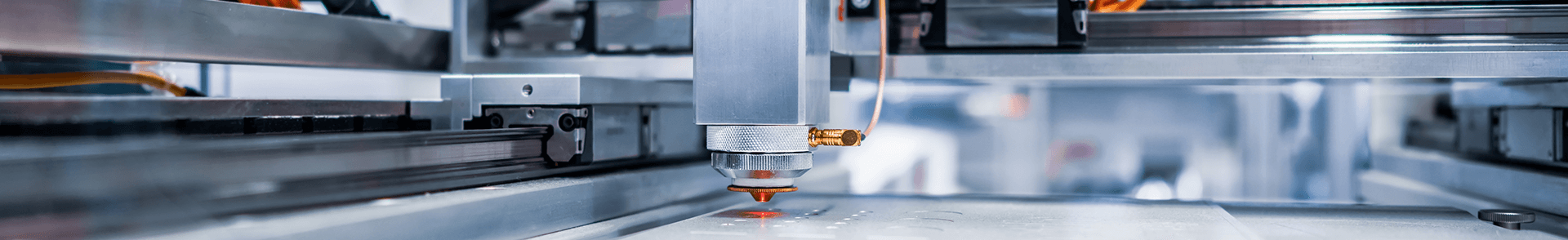
How does laser marking work?
Laser marking uses a laser beam to emboss permanent markings on the materials. It can mark any metal, plastic, or organic material.
With a suitably powerful light beam, the product is heated, changing the appearance of the surface in specific locations, allowing information for traceability or designs to be reproduced on the surface.
As this is a “no-contact” technology, laser marking allows not only deep engraving and product identification, but also extremely clean, detailed processing which can ensure a high-resolution finish without ruining the materials’surface with burrs or abrasions.
Laser marking is also designed to resist acids, corrosion, and weathering. Another advantage is the speed of this technology. Laser marking machines can quickly and accurately engrave any material or surface, increasing the company’s productivity while guaranteeing maximum safety for the equipment users.